| c.2000 | ARCHAIC PERIOD ends. In Americas from 10-8000, characterized by sedentary farming. | 2000, but date varies across Americas: wiki |
| c.2000 | NORWOOD Culture begins in the Apalachee region, a forested and hilly part of north Florida until 500. Triangular projectile point knives with notches for attaching stone implements to shafts. Archaic cultures began using hand held spears to atlatls. | 2000 wikAPNA no date: wikNC |
| c.2000 | MESO-AMERICA: ARCHAIC PERIOD ends. Began 3500. PRE-CLASSIC Age Formative Period begins until 200CE. Early Formative Period begins until 900. Manufacture of ceramics is widespread, cultivation of maize and other vegetables becomes well-established, society starts to become socially stratified. Capacha culture civilizes Mesoamerica, and its pottery spreads widely. Heavy concentration of pottery on Pacific Coast. Maize and pottery in Panama. Unknown culture in La Blanca and Ujuxte, Monte Alto culture, Mokaya culture. | 2500 ttco 2000 mxfld, dlyks, wikHA, wikMC Preclassic begins 1800: wikMC |
| c.2000 | MAYAN Pre-Classical period begins until 250CE. Grows maize, beans, squash and cassava (manioc). | 2000 wikMC 1800 hstM |
| c.2000 | HUASTEC people split from the Proto-Mayas but probably don't travel far from the Guatemala-Chiapas borderlands. Huastecs construct temples on step-pyramids, carve sculptures, produce elaborately painted pottery, build cities, yet usually wear no clothing. They are known for musicial abilities. | 2000 wikHu |
| c.2000 | South America: LATE PRECERAMIC Period from 5000 ends. As people become sedentary, populations grow, leading to areas of resource shortage. Peru: COTTON PRECERAMIC Period from 2500 ends. Domesticated cotton used to produce fine nets to catch anchovy beyond subsistence requirements. Much surplus was used to support construction of monumental architecture, e.g. at El Paraíso and Aspero. |
2000 jrnk |
| c.2000 | Andean CAMELIDS, already domesticated in Junín puna and highlands of Osmore basin, now domesticated in high deserts of north Chile. | 2000 jrnk |
| c.2000 | VALDIVA, a coastal society in Ecuador, has maize and pottery similar to the Jomon pottery of Japan. | 2000 mxfld |
| c.2000 | PERU: 1st metal working. | 2000 TAWH 16 1500 PW 14 |
| c.2000 | PERU: Earliest ceramics and large scale maize cultivation. | 2000 PW 14 |
| c.2000 | PERU: Guinea pig domesticated. | 2000 TTS |
| c.2000 | MAIIZE cultivation begins in Brazil. | 2000 jrnk |
| c.2000 | COTTON: Wrappings used in Peru and clothing in lower central Andes. (See India 2000, Scandinavia 1000) |
2000 SHT 1-449, mxfld |
| c.1950 | DOMESTICATED ANIMALS in South America. | soon after 2000 mxfld |
| c.1900 | TLAPACOYA, southeast of Mexico City, founded. Lasts until 450. | 1900 wikMC |
| c.1800 | ALEUTIAN TRADITION from 2500 ends. Artifacts of chopped stone, unlike the more common slate tools. Objects made by core & flake method, bifacially carved projectile points. People lived in semi-subterranean winter houses of driftwood, whale bone, and peat. They used kayaks, atlatls and harpoons to kill sea mammals. | 1800 wikAP, wikAT |
| c.1800 | CAPACHA culture begins on the Colima coast of west Mexico until 900. Earliest widespread cerramic complex of Meso-America: stirrup jars, belted jars, water jars and composite forms. | 1800 wikMC |
| c.1800 | MAYA settlement begins in Soconusco. | 1800 wikM |
| c.1800 | Sedentary village life is widespread. Pottery is abundant. | 1800 eah |
| c. 1800 | VALDIVIA culture of Ecuador from 3500 ends. Communities of sedentary farmers, fishermen, and deer hunters living in houses built in a circle or oval around a plaza. They grew maize, kidney beans, squash, cassava, hot peppers, and cotton. | 1800 wikPCe, wikVC |
| c. 1800 | In the Casma/Sechin culture 3600-200 of Peru, the Preceramic Period ends. Began 3000. Noted for growth of coastal settlements of Huaynuna, with a settlement dated at 2900, and Las Haldas with a settlement is dated at 2200. Both Huaynuna and Las Haldas are located more than 12km from the irrigable lands of the Casma River Valley. Fishing was their main means of subsistence. Initial Period begins until 900. Noted for woven textiles, pottery, adoption or expansion of canal irrigation for agriculture, and construction of pyramids and plazas. Sites include Sechin Bajo and Cerro Sechin, which date back to the Preceramic Period, but are reconstructed and expanded during this phase. |
1800 wikCSc |
| c.1800 | NORTE CHICO civilization of north-central coastal Peru from 3000 begins to decline. Irrigation-based agriculture. People move to more fertile ground. | 1800 wikHA, wikNC ends: wikPCe |
 Main pyramid at El Paraíso photo Yhhue91 |
| c.1800 | EL PARAISO, a U-shaped site of central coastal Peru occupied from 3500 abandoned. Function disputed, possibly an economic or religious centre, or both. Has no ceramics during its main occupation period. | 1800 EPP |
| c.1750 | JAKETOWN, Mississippi: occupied by a mound builder culture until 1500CE, making it one of the oldest continuously inhabited sites in the area. | 1750 wikJake |
| c.1750 | CANAL built in Rimac valley northeast of Lima Peru. | 1750 TTT |
| c.1730 | Chavin-like construction begins at Quebrada until 850. | 1730 jqj |
| c.1700 | Chavin coastal monumental centers flourish until 900. | 1700 jqj |
| c.1628 | Evidence of Thera eruption appears in glacial strata in Greenland. | 1645 TTS 1628 wikME 1520 TTPC 1500 MCAW 32, OCD 1060, TAWH 66, mxfld |
| c.1600 | Villages along Coazacoalcos River on Gulf of Mexico thrive on abundant river resources and fertile soils. | 1600 eah |
| c.1600 | SOCONUSCO coastal strip in south Chiapas: Villages increase. | 1600 eah |
| c.1600 | RUBBER BALLS used in El Manati, an Olmec sacrificial bog 10km east of Tenochtitlan. These balls predate the earliest ball court yet discovered. | 1600 wikO |
| c.1600 |  Earliest BALL COURT yet discovered at Paso de la Amada in Chiapas. 80m × 8m flat playing alley defined by 2 flanking earth mounds with 'benches' running along their length. Earliest BALL COURT yet discovered at Paso de la Amada in Chiapas. 80m × 8m flat playing alley defined by 2 flanking earth mounds with 'benches' running along their length. |
1600 wikO 1400 wikMBC Drawing GNU FDL |
| c.1550 | FIRE made by wooden hand-drill depicted on Mexican manuscript. | 1550 SHT 1-224 |
| c.1500 | British Columbia and Washington state: People settle in villages and catch salmon, but do not practice cultivation. | 1500 mxfld |
| c.1500 | ENCINITAS Tradition (Millingstone Horizon) of California from 5500 ends. Sites are at San Luis Obispo County, Santa Barbara County, and Ventura County. CAMPBELL Tradition (Intermediate Horizon) begins until 1000CE. |
1500 wikAP, wikMH |
| c.1500 | COCHISE Tradition (part of Picosa culture) in southwest US 5000-200, CHIRICAHUA phase from 3500 ends. Chiricahua tools have different projectile points and many seed-processing artifacts. SAN PEDRO phase begins until 200. Has large projectile points with corner or side notches and straight or convex bases. Sites contain oval pithouses, requiring effort to build. Some houses group in small villages. A new and more vigorous strain of MAIZE arrives from Mexico. Kidney beans appear. As agriculture makes easier living, pottery develops and soon figurines of people and animals. |
1500 wikAP, wikCT 1000 mxfld |
| c.1500 |  POVERTY POINT in Louisiana: Late Archaic mound-builder construction (2500 - 1000). Area: more than one square mile, six earthwork crescent ridges built concentrically interrupted by radial aisles. POVERTY POINT in Louisiana: Late Archaic mound-builder construction (2500 - 1000). Area: more than one square mile, six earthwork crescent ridges built concentrically interrupted by radial aisles. |
map Maximilian Dorrbecker 1500 wikMB |
| c. 1500 | 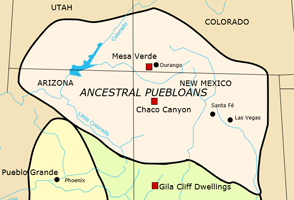
 PUEBLO Culture: Early Basketmaker Era from 7000 ends. Nomadic hunter gatherers in the Colorado Plateau, living in easily built homes. They generally inhabit rock alcoves or live in the open in brush shelters and lean-tos. Dwellings are made by digging a shallow basin and building a frame of wooden logs in the shape of a cone, dome or tent. Frames are covered with brush and earthen daub sealant for protection. Fire pits are sometimes used inside homes. The shallow-basined lodgings are considered a precursor to Basketmaker pit-houses.
PUEBLO Culture: Early Basketmaker Era from 7000 ends. Nomadic hunter gatherers in the Colorado Plateau, living in easily built homes. They generally inhabit rock alcoves or live in the open in brush shelters and lean-tos. Dwellings are made by digging a shallow basin and building a frame of wooden logs in the shape of a cone, dome or tent. Frames are covered with brush and earthen daub sealant for protection. Fire pits are sometimes used inside homes. The shallow-basined lodgings are considered a precursor to Basketmaker pit-houses.Early Basketmaker-II Era begins until 50 CE. Begins with maize cultivation, though not dependent on agriculture until c.500. They live in a range of structures including small family pit houses, larger structures to house clans, grand pueblos, and cliff-dwellings. Projectile points, "2 rod and bundle" basketry style, and other similarities exist between Basketmaker-II and the San Pedro stage of the Cochise tradition. They are called Anasazi "ancestors of enemies" by the Navajo. |
cave art J.Q. Jacobs map Arkyan 1500 wikAEBE, wikAP 1200 wikLPC 12th cen. wikAP |
| c.1500 | Dzibilchaltun in northern Yucatan is settled by Mayas and occupied by Mayas continuously. | 1500 mxfld |
| c.1500 | TEHUACAN Valley in Puebla: AJALPAN cultural phase begins until 850. Complex village life, pottery, elaborate religious rituals, and intricate social organization. | 1500 mxfld |
| c.1500 | Meso-America: FORMATIVE PERIOD begins until 400. | 1500 wikO |
| c.1500 | MESO-AMERICA: maize-farming is the basis of life. | 1500 mxfld |
| c.1500 | GUATEMALA: Iridescent ceramic pottery begins at La Victoria until 800. | 1500 mxfld |
| c.1500 | CUPISNIQUE Culture on north coast of Peru begins until 500. Has a distinctive adobe architecture, but shares artistic styles, gods, and religious symbols with the later Chavin culture. | 1500 wikPCP 500 wikCps |
| c. 1500 | CERRO SECHIN in Casma River Valley 13km from coast, in north Peru from before 2000, abandoned. Complex covers 3-400 acres. Contained walled enclosures around dwellings as well as temple platforms, several buildings, of clay and stone. Main building is 51 sq m and 4m high. Temple is rectangular with rounded corner, constructed of conical adobes. The stone building has a lithic block facade decorated with relief carvings representing warrior-priests and mutilated bodies. 300 bas-reliefs show axe-wielding warriors, body parts, and victims, who are decapitated and mutilated. Cerro served as a central administration place for production, distribution and food, and a worship and ceremonial center.
The stone building has a lithic block facade decorated with relief carvings representing warrior-priests and mutilated bodies. 300 bas-reliefs show axe-wielding warriors, body parts, and victims, who are decapitated and mutilated. Cerro served as a central administration place for production, distribution and food, and a worship and ceremonial center. |
1500 wikCS 1200 jqj left AgainErick right AgainErick |
| c.1475 | DOGS are the only domesticted animals in North America. | 1500-1451 TTS |
| c.1450 | North American Indians grow maize, beans and squash. They have surplus food and time needed for communal activities. | after 1500 mxfld |
| c.1450 | EL PARAISO in the Chillon River Valley of Peru from 2000, and all the bean planter villages of Peru abandoned. Reason unknown. | 15-1400 mxfld |
| c.1400 | SUNFLOWERS cultivated in North America. | 1400 TTS, TTT |
| c.1400 | OLMEC culture begins until 400, emerging at Tenochtitlan (San Lorenzo) near the coast in southeast Veracruz until 900. | 16-1500 wikPCe 1400 wikMC, wikO 1250 mxfld 1200 wikHA |
| c.1400 | ZAPOTEC settlement founded at SAN JOSE MOGOTE in Oaxaca, Mexico. It lasts until 500. | 1500 wikSJM 1400 wikMC |
| c.1400 | SOCONUSCO villages in south Chiapas, Mexico: Luxury goods such as ceramic figurines, stone bowls, and greenstone beads are placed in graves. | 1400 eah |
| c.1400 | Sophisticated CERAMICS made in Highland villages of central Mexico, notably small, detailed female figurines. | 1400 eah |
| c.1400 | TLATILCO and TLAPACOYA villages in the Basin of Mexico and Las Bocas in western Puebla, establish precedence over their neighbors. | 1400 eah 1350 wikMC |
| c.1350 | First public building in Oaxaca Valley is constructed at San Jose Mogote. It is stuccoed wattle-and-daub with limed walls and floors built on a platform foundation. | 1350 eah by 1200 mxfld |
| c.1350 | Olmec settlement at TEOPANTECUANITLAN, in Guerrero begins until 700. | 1350 wikMC |
| c.1300 | INDPENDENCE I Culture living north of Independence Fjord in Greenland from 2400 ends. | 1300 wikSqC 1000 wikI1C |
| c.1300 | HUASTECS move west to Veracruz. |  |
by 1300 wikHu |
| c.1300 | HUASTECS move north from Veracruz to Huasteca. | retouched Raxerios 1500-900 wikHP |
| c.1300 | Some villages in Oaxaca Valley are agriculture dominant. Villages contain 10 to 20 single family units made of wattle and daub, all opening into a common plaza. | by 1300 mxfld |
| c. 1300 |  CHORRERA Culture begins in Ecuador until 300. Spans Pacific lowlands to Andean highlands, and into south Colombia. Noted for ceramics, featuring whistling animal and plant effigies, stirrup spout vessels, human figurines made from molds. Utilitarian pottery is thin with decorated walls and red or black slips highly polished. Surfaces of bowls, bottles, ollas, and other ceramic pieces are incised, painted, pattern burnished, or decorated with rocker stamps. Chorrera is divided into regional phases: CHORRERA Culture begins in Ecuador until 300. Spans Pacific lowlands to Andean highlands, and into south Colombia. Noted for ceramics, featuring whistling animal and plant effigies, stirrup spout vessels, human figurines made from molds. Utilitarian pottery is thin with decorated walls and red or black slips highly polished. Surfaces of bowls, bottles, ollas, and other ceramic pieces are incised, painted, pattern burnished, or decorated with rocker stamps. Chorrera is divided into regional phases:
|
left Vassil right Helvetiker 300 wikChC |
| c.1300 | Pottery first evidenced in western Peru. | 1300 mxfld |
| c.1200 | OLMEC civilization appears without known antecedents in the humid, low-lying, forest region of south Veracruz and west Tabasco on the Gulf of Mexico. Capital at Tenochtitlan 1400-900. Olmecs build flat-topped pyramids, write in hieroglyphs, develop a calendar, and predict movements of planets. Olmec civilization ends 400. | 1400 TTT 1200 PW 15, mxfld, wikHA 1150 TAWH 16 |
| c.1200 | Calendar V developed by Olmecs (later called the Mayan Calendar). (See Babylonian 1790, Egyptian 1500, Gezer 950, Babylonian 747) |
2000 tmdt 1400 TTT 1200 mxfld |
| c.1200 | CUICUILCO on south shore of Lake Texcoco in southeast Valley of Mexico, 1st occupied, but not founded as a city until 800. | 1200 wikCui |
| c.1200 | Chavin de Huantar Peru, occupied 3000-400: Major building phase begins until 750. | 1200 wikCdH |
| c.1190 | Monumental Chavin construction begins at Las Haldas south of Casma River until 900. | 1190 jqj |
| c.1150 | OLMECS build large ceremonial center at Tenochtitlan. Most pure Olmec monuments and structures built from now onward. | 1250 TTT 1150 mxfld |
| c.1100 | HUASTEC people arrive at present location in San Luis Potosi and Veracruz. | 1100 or later: wikHu |
| c.1100 | Canoe comes into regular use in east USA. | 1100 iu |
| c.1050 | BELLE-GLADE culture begins near Lake Okeechobee in Florida until 1700. Circular ditches appear early. Contains mounds, earthworks, undecorated pottery. | 1050 wikAP 1000 wikBG |
| c.1050 |  Olmec Colossal Head 3, (San Lorenzo Monument 3). 1.78m high by 1.63m wide by 0.95m deep and weighs 9.4 tons. Found face down 0.8km southwest of the main mound at San Lorenzo. Its original location is unknown. Olmec Colossal Head 3, (San Lorenzo Monument 3). 1.78m high by 1.63m wide by 0.95m deep and weighs 9.4 tons. Found face down 0.8km southwest of the main mound at San Lorenzo. Its original location is unknown. |
photo frida27ponce 1200-900 wikMsA |
| c.1050 |  Olmec Baby Figure. Olmec Baby Figure. |
photo Flickr 1200-900 wikMsA |
| c.1050 |  Tlatilco Contortionist. Tlatilco Contortionist. |
photo GNU FDL 1300-800 wikTlt |
Americas 1000-500
V